Cost estimator
Looking to install EV chargers in your multi-residential or commercial building but unsure what’s required and how much it might cost? EVIAM’s budget estimator will guide you through the steps.
Introduction
Installing a single EV charger at a house is straightforward.
But installing EV chargers in apartment towers or commercial sites is more complicated:
- What’s the impact on electricity usage in common areas?
- Could the building’s peak electrical load be exceeded?
- Is there sufficient switchboard, distribution board and cabling capacity?
- How will residents be billed for their electricity usage?
- Will the EV charger(s) be accessible by the public, and if so, how will they pay?
These are the problems that EVIAM solves. Call us on 1300 038 669 for immediate help!
Frequently asked questions
- Master Switchboard (MSB) connected to the existing MSB
- Distribution board(s) (DB’s) connected to the new MSB. Each DB can service a maximum of 24 car parking bays
- Australian compliant meters for each connected EV charger
- Load management system (LMS) to manage peak demand
- Data cables from the LMS to the EV chargers
- Power cables from the new MSB via the DB’s to the EV chargers
- Cable trays
Following installation, a system integrator is needed to configure and commission the entire installation.
No, other factors are:
- Chargers don’t charge at maximum power continuously. For example, DC chargers charge rapidly until the battery reaches 80-90% capacity, then slow significantly for the remaining 10-20% charge
- The optimum outside temperature range for charging is 20 – 30° C – outside this range charging can take longer
- EV’s have different onboard circuitry which can affect the maximum charging speed
- A building may have a Load Management System which monitors and limits power consumption during peak demand
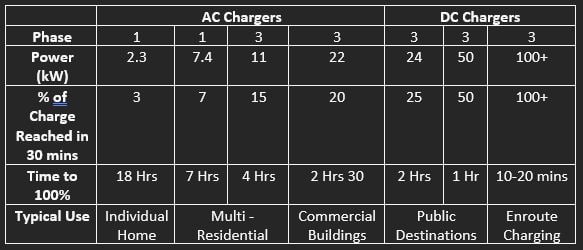
- Power ratings of AC chargers are typically:
- Single phase chargers:
- 3kW (equivalent to a standard wall socket)
- 7.4kW
- 3 Phase chargers:
- 11kW
- 22kW
- 3 Phase chargers:
- 24kW
- 50kW
- 100-350kw
- Single phase chargers:
- Chargers connect via one (“single phase”) or three (“3 phase”) conductors. A single conductor is less efficient, more prone to power interruption, and can manage less power than 3 conductors.
The Australian power grid supplies Alternating Current (AC).
Electric Vehicles and Plug-In Hybrids have onboard circuitry that allows then to be charged from either AC or Direct Current (DC) power sources.
An AC charger connects the AC supply from the grid to the vehicle’s on-board circuitry (“rectifier”) where the current is converted to DC for charging the vehicle’s battery.
A DC charger contains an inverter which converts the grid’s AC current to DC. A DC charger bypasses the vehicle’s rectifier and connects directly to the vehicle’s battery for charging.
Budget Estimator Tool
Installing a single EV charger at a house is straightforward.
Step 1
Select the power rating of your EV charger(s). This will determine how quickly your vehicles will charge (and affect the estimated price of the works). Read our FAQ’s if you need help in determining your needs
Step 2
Select the nature of the car-parking area at your building. Car-parking which is open to the environment requires (more expensive) weather resistant chargers. Multi-level car-parking requires cabling to penetrate concrete flooring.
Step 3
Estimate the new electrical infrastructure that will be required (master switchboard, distribution boards, Load Management System, cabling/ducting.
Step 4
Get your answer!
Book a site visit
Want to know more about what your building needs?
Schedule a free on-site inspection with one of our technicians.